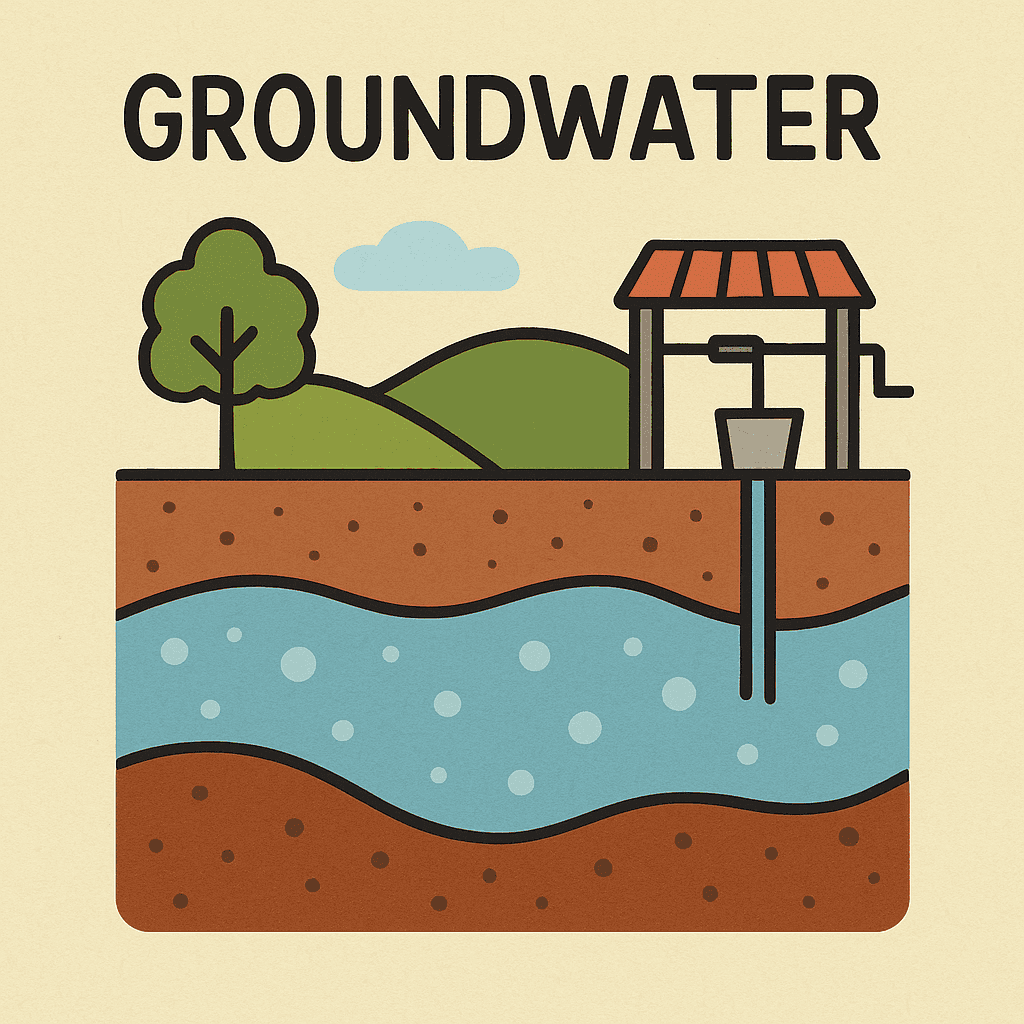
Meaning
Groundwater refers to water that exists below the Earth’s surface, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. It is stored in aquifers and supplies wells and springs.
Grammar and Usage
-
Part of speech: Noun (uncountable)
-
Used to describe underground water resources.
-
Often used in environmental, geological, and hydrological contexts.
-
Typical structures:
- "groundwater level"
- "groundwater contamination"
- "groundwater recharge"
Common Phrases
- groundwater table – the level below which the ground is saturated with water.
- groundwater recharge – the process by which water seeps into the ground to replenish aquifers.
- groundwater contamination – pollution of underground water resources.
- groundwater depletion – reduction of groundwater due to overuse.
Collocations
- groundwater resources
- groundwater flow
- groundwater supply
- groundwater pollution
- groundwater management
Examples
- The city depends heavily on groundwater for its drinking water supply.
- Farmers often use wells that draw water directly from groundwater.
- Industrial waste has caused groundwater contamination in the area.
- Climate change is affecting the natural groundwater recharge cycle.
- Over-pumping has led to groundwater depletion in many regions.
- Scientists monitor groundwater levels to predict drought conditions.
- The village built a well to access clean groundwater.
- Protecting groundwater resources is essential for future generations.
Synonyms or Related
- aquifer water
- subsurface water
- underground water
Antonym
- surface water (e.g., rivers, lakes, ponds)